Have you ever thought about the importance of those colorful optic fiber cables that run through your neighborhood? Furthermore, in addition to their sleek and modern look, the color coding of fiber optic cables plays a critical role in enhancing network performance and assisting smooth communication. Therefore, in this informative blog post, we will explore the fiber color code and its meanings. Whether you are a network engineer, a technology enthusiast, or just curious about the digital infrastructure that surrounds you, this post will clarify the hidden significance of those bright optic fibers. Ultimately, let’s explore and discover the secrets of the fiber color code!
What Is Optical Fiber and How Does It Work?
Before knowing about fiber color code, let’s begin by understanding Fiber optics or optical fiber. Basically these are a special type of cable that uses light to send data. Specifically, optical fiber technology involves thin strands of glass—roughly the same width as a human hair—that are grouped together to create fiber optic cables. Consequently, these cables transfer light signals from one spot to another, carrying data like internet, phone, or TV signals. Essentially, optical fibers work like highways; instead of cars, they transport light beams loaded with data. To sum it up, optical fibers are super-fast pipes for data, thereby making it possible to transmit data quickly over long distances.
Uses of Optic Fibers in Technology
Fiber optics serve a bunch of different uses, such as:
- Internet: They provide super fast internet speeds, making downloads and streaming a breeze.
- Telecommunications: They’re used for phone lines and video chats.
- Television: They send high-quality video signals for TV shows.
2 Different Types of Optic Fibers
You must first be aware of types of optical fibers then only you can better understand the fiber color code. This is because the color of optic fiber depends upon the type used. Basically, two key types of optical fibers are used:
|
Type of Fiber |
Core Size | Light Transmission | Distance |
Use |
|
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) |
Small (around 9 µm) | Single light path (mode) | Long-distance (up to 100 km or more) |
Telecom, cable TV, internet, long-haul networks |
|
Multimode Fiber (MMF) |
Larger (50 µm or 62.5 µm) | Multiple light paths (modes) | Short-distance (up to 2 km) | Local area networks (LANs), data centers |
We pick these fibers depending on how far we need to communicate and the bandwidth we need.
Why Do We Need Fiber Color Code?
The color of the optical fiber cable is important because it indicates the cable’s purpose. For example, some cables are meant for data signals (like internet connections), while others, on the other hand, handle voice signals (like phone calls). Furthermore, the different fiber optic color codes help you quickly identify them; consequently, this makes installation and maintenance a lot less confusing.
Who Decides Fiber Color Code?
An important question is whether manufacturers color optical fibers as they wish or if they stick to a standard. In this regard, the Fiber Optic Association (FOA) has set up a system to assist engineers and technicians in identifying various fiber optic cables. For instance, the TIA-598 standard fiber color code is widely used, particularly in the U.S., thereby simplifying recognizing and dealing with these cables.
How Does the Color-Coding System Work in Fiber Optic Cables?
Now all three parts, namely the outer cable jacket, inner fiber strand, and connectors , are colored. Here is how and why they are colored.
- Outer Cable Jacket: First and foremost, the external layer of the cable is color-coded to indicate the type of fiber. For instance, yellow denotes single-mode fibers (SMF), whereas orange signifies multimode fibers (MMF). Moreover, the color of the jacket also indicates the cable’s function, such as data or voice transmission.
- Inner Fiber Strands: Next within the cable, each fiber is color-coded for easier identification, particularly in multi-fiber cables. Generally, colors are paired; for example, the first fiber may be blue and the second orange. Consequently, this pairing aids technicians in accurately matching fibers during connections or troubleshooting.
- Connectors: At last, the connectors that connect fiber optic cables to devices are also color-coded. In particular, the color of the connector shows the type of fiber and the polish applied. For example, blue connectors are used for single-mode fibers, while green connectors indicate a special polish known as APC (Angled Physical Contact), which minimizes signal reflection.
As a result, these fiber color codes help you quickly spot and sort out fiber optic parts.
Understanding Colors Through Fiber Color Chart
Fiber color code can be well understood with the help of a fiber color chart. Let’s see in detail.
-
Cable Jacket Color Code (Outer Layer)
The color of the outer jacket shows what type of fiber’s inside.
- Single Fiber Type: Firstly If the cable has just one type of fiber, the jacket sticks to standard colors.
- Multiple Fiber Types: In contrast for cables that have different types of fibers, the jacket might have printed info that tells you the number and types of fibers. For instance, 24 Fiber 16 x 9/125, 8 x 50/125 means there are 24 fibers total—16 single-mode (9/125µm) and 8 multimode (50/125µm).
- Standard Color Coding: Additionally Regular fiber optics color coding follows systems like TIA-598 for typical telecommunications.
- Military color coding: On the other hand, these follow specific standards for better durability and easy identification in tactical situations.
|
Fiber Type |
Non-Military Color |
Military Color |
|
OM1 (62.5/125µm Multimode) |
Orange | Slate |
| OM2 (50/125µm Multimode) | Orange |
Orange |
|
OM3 (50/125µm Laser-Optimized Multimode) |
Aqua | Undefined |
| OM4 (50/125µm Laser-Optimized Multimode) | Aqua/Violet |
Undefined |
|
100/140µm Multimode |
Orange | Green |
| OS1/OS2 (Single Mode) | Yellow |
Yellow |
|
Polarization Maintaining Single Mode |
Blue |
Undefined |
-
Inner Fiber Color Code (Inside the Cable)
In multi-fiber cables, every fiber is color-coded to ensure everything stays organized. For example, the usual color system for the first 12 fibers goes like this:

- Blue
- Orange
- Green
- Brown
- Slate (or Gray)
- White
- Red
- Black
- Yellow
- Violet
- Rose (or Pink)
- Aqua (or Light Blue)
Note: If there are more than 12 fibers, in such cases the color pattern repeats.
-
Fiber Color Code For Connectors
The connectors on the ends of fiber optic cables come in different colors. Moreover, these connectors are what link the fiber to devices or other cables. Specifically, the colors tell you the type of fiber they’re for and how the connector looks:
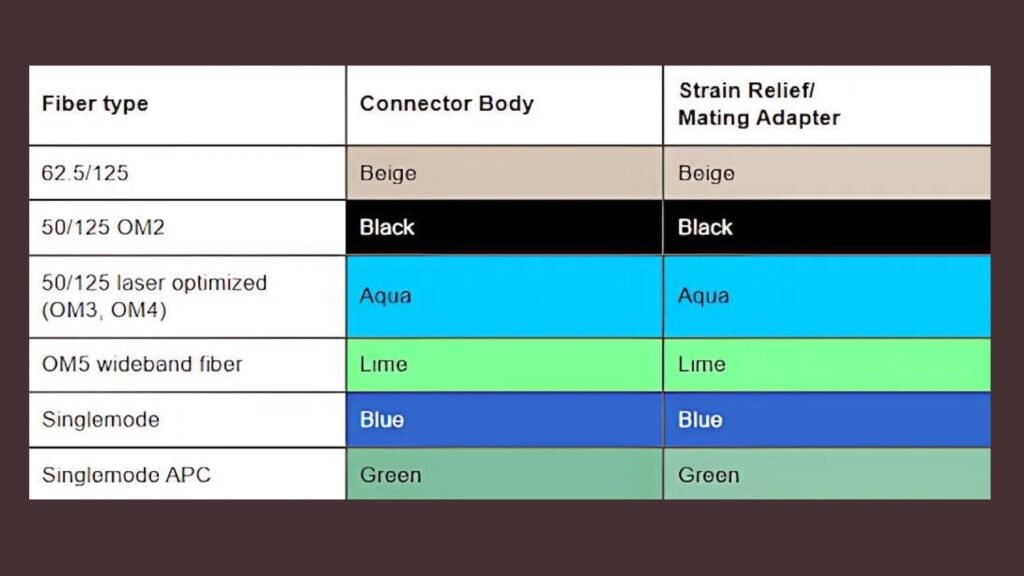
- Beige or gray connectors are used for multimode fiber (short-distance).
- Blue connectors are used for single-mode fiber (long-distance).
- Green connectors are for a special type of single-mode fiber that has a different shape.
Meaning Of Fiber Optic Cable Colors
As we have already learned, the fiber color chart is super handy for spotting if the cable is for long-range or short-range use; that is to say, it’s for hooking up devices inside a building or for communicating over long distances between cities. Now, let us see what the meaning of each fiber optic cable colors:
|
Color |
Meaning |
| Blue |
It stands for multimode fiber used for shorter-distance data transmission. |
|
Orange |
It means single-mode fiber for long-distance communication. |
| Yellow |
Indicates single-mode fiber for long-distance communication between cities. |
|
Aqua |
Represents high-speed multimode fiber used in data centers for fast networks. |
| Green |
Shows special long-distance single-mode fiber for outdoor use. |
| Violet |
Signals laser-optimized fiber for high-performance systems. |
Consequently, knowing these color codes helps you keep fiber optic setups organized and makes sure you’re using the right cable for the job.
Wrapping Up
To sum up, getting a grip on why color coding matters in fiber optic cables is, therefore, super important for keeping things running smoothly. Specifically, the colors on the cable jacket, the inner fibers, and the connectors help techs figure out what kind of fiber they’re dealing with and how to hook it up right. Consequently, this cuts down on mistakes during the setup and makes maintenance a breeze, especially in big projects.
FAQ
- Why is color-coding critical in fiber optics?
Color-coding is super important because, ultimately, it helps you easily spot cables and what they do. Consequently, this makes installation a breeze, troubleshooting easier, and it also helps techs keep track of complicated systems.
- Do color codes change depending on the manufacturer?
Yes, they can vary; however, the Fiber Optic Association (FOA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) push for standard systems like TIA-598 in order to keep things consistent across the industry.
- Can you color-code fiber optic cables for specific fields or uses?
Absolutely! In fact, certain industries can create their own color-coding systems to fit their needs. For example, they might use different colors for cables in hospitals for surgeries versus regular telecom, thereby making it safer and easier to identify in critical moments.